The Robot Revolution
Caoimhghin Ó Croidheáin | 03.05.2013 11:05 | Globalisation | Social Struggles | Technology

John Kay inventor of the Fly Shuttle, by Ford Madox Brown.

Desk Set (1957)

Factory robots (ABB robot IRB 6400)

Tokyo Tower robot Tawabo guides visitors in four languages
The current crop of robotic developments and inventions have produced a huge ‘aaw’ factor as dancing, walking and talking, ‘Livin’ Robots’ have entertained people all over the world. However, this is merely a transition period of finding general acceptance by an unsuspecting public who are unaware of how close they are getting to a labour crisis of disastrous proportions.
The recent history of machines and robotic devices shows us that the world of technological advancement steams ahead with or without the consent of the workers whose jobs are ultimately displaced forever. How did we get from Luddite frame breaking to ‘Loving the Alien’?
There is what could be described as three levels of the technologisation of work,
(1) Basic Machines (Simple and Engine),
(2) Complex Machines (Electrical, Electronic and Computing), and
(3) Sophisticated Machines (Anthropomorphic Robots). In each case technologisation has brought benefits as well as disaster. However, we are reaching a point where further technologisation can only exacerbate the global problems of mass unemployment, climate chaos, depletion of the world’s resources and exceed the planet’s capacity for recovery.
(1) Basic Machines (Simple and Engine)
“Surely my lord however we may rejoice in any improvement in the arts which may be beneficial to mankind, we must not allow mankind to be sacrificed to improvements in mechanism. The maintenance and well-doing of the industrious poor is an object of greater consequence to the community than the enrichment of a few monopolists by any improvement in the implements of trade, which deprives the workman of his bread, and renders the labourer ‘unworthy of his hire.’” Lord Byron’s speech to the House of Lords February 27, 1812, at the height of Luddite activities in Yorkshire, England. [1]
Warring with Rude Nature
The introduction of machines during the Industrial Revolution became the focus of anger of the English textile artisans in the early 19th Century. The new stocking frames, spinning frames and power looms enabled the factory owners to replace artisans with cheaper low-wage labourers. This resulted in the unemployed textile artisans coming together and attacking the factory machinery and burning down mills. Known as Luddites, these men and their supporters battled with the industrialists and the British Army from 1811 to 1817. The government eventually quashed the movement with show trials resulting in many penal transportations and executions. [2]
The significance of the introduction of machinery and the long term effects of the Luddite movement was not lost on Friedrich Engels, who wrote in 1845:
“The service which machinery has rendered the workers is simply this: that it has brought home to their minds the necessity of a social reform by means of which machinery shall no longer work against but for them. […] Every new advance brings with it loss of employment, want, and suffering, and in a country like England where, without that, there is usually a ‘surplus population’, to be discharged from work is the worst that can befall the operative.” [3]
The struggle against the machines soon became a struggle for control of the machines.
(2) Complex Machines (Electrical, Electronic and Computing)
“When was the last time a real receptionist texted you about an important call? Or worked 24/7 (there’s labor laws against that)? A virtual receptionist works for peanuts and doesn’t demand benefits.” [4]
The computers are coming
For the next one hundred years the existence of factories became accepted and trade unions took on the challenge of resistance to the factory owners. However, the spread of the machines in the workplace was really only beginning. In 1951, the first commercial business computer was developed in the United Kingdom by the J. Lyons and Co. catering organization. It was known as the ‘Lyons Electronic Office’ – or LEO for short. The LEO computer was further developed and then widely used during the 1960s and early 1970s. [5]
During a visit to USA Lyons’ managers met Herman Goldstine, one of the original developers of ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer), the first general-purpose electronic computer (although it had no stored program). [6] In 1953 IBM (International Business Machines) introduced the 701 to the public, their first electric computer and first mass produced computer. [7] Avoiding the type of knee-jerk rejection of new technology by the early Luddites, a softly-softly approach to mass acceptance of computers was created through information films such as “Electronic Computers Improve Management Control” (UCLA 1957) lauding their efficiency and advantages, and cinematically by films such as Desk Set (1957) summarised as:
“Richard Sumner (Spencer Tracy), the inventor of EMERAC (an allusion to the early computers UNIVAC and ENIAC) and an efficiency expert, is brought in to see how the library functions, to figure out how to ease the transition. […] When they find out the computers are coming, the employees jump to the conclusion the machines are going to replace them, whereas they are merely intended to help ease the research.” [8]
When the ‘silly computer’ fires everyone in the building by mistake, Sumner has to explain that EMERAC‘was never intended to take over’ to ease the anxiety of workers. The support of IBM for the film is acknowledged in the opening credits: “The filmmakers gratefully acknowledge the cooperation and assistance of the International Business Machines Corporation.” [9] The optimistic message of Desk Set had changed by the late 1960s with the Jerome Epstein film The Adding Machine (1969) about ‘an accountant whose job is about to be taken over by a computer [and who] starts to re-examine his life and his priorities.’ [10] By the 1980s, according to Alan Nasser, the effects of the introduction of computers were such that:
“An office in the 1980s employing 40 people working without computers may require, in the early 1990s, only 4 workers using 4 computers. The productivity – output per unit of labor input – of the office can be further enhanced not by adding skilled workers nor by replacing less productive workers with more productive computers, but by replacing less powerful computers and software with more powerful ones. In the initial case, actual workers were replaced by computers. In the latter case potential workers were kept out of the workplace by better computers.”
Over the last few decades we have seen the introduction of technology changing working class jobs such as the use of hand scanners and self-service check-out machines in supermarkets, stamp machines in post offices, electronic toll collection, automated attendants in telephony, virtual receptionists, ticket machines in car parks and train stations and swiping machines and integrated security systems affecting security guards.
More and more middle class jobs are under threatwith the Automated Teller Machine (ATM) in banks, the use of the internet for shopping, translation, and teaching.
In the same period of time the technologisation of factories has seen the introduction of factory robots working on fully automated production lines and then packaging and palletizing, automated guided vehicles (AGVs) transporting goods around warehouses, automated fruit harvesting machines and telerobots.
In fact, we are mesmerized by the potential use of robots. In an article by Aaron Saenz he notes the “awe-inspiring, perhaps even frightening” aspects of modern manufacturing:
“The factories of today have some human workers, but huge portions of assembly lines are 100% mechanized. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics expects automotive jobs to decline 18% by 2018 despite expected increases in production. Robots eliminate the need for more workers. Before you lament the loss of jobs, take a moment and watch how robots earn their role every day in the workplace. Incredible!”
Our fascination with robots is overcoming our cautious nature as we are once again presented with images of the new ‘silly machines’.
(3) Sophisticated Machines (Anthropomorphic Robots)
“Imagine a world where the robots did all the work. They tend the crops, sew the clothes, cook the food, drive the trucks, and work on all the assembly lines in all the world’s factories. In this world, everything would be a lot cheaper because labor costs would drop to zero. In fact, there’d be a startling abundance of stuff. And people would be freed up to do things other than work. We could use our time to explore, create, perform, craft, mingle, and so on because we wouldn’t have to work to produce the necessities or luxuries of life; the robots would be taking care of that.” [11]
Fascinating Robots
The titles of the videos about the latest robots (Dancing Robots, World’s Top3 Humanoid Robots, Most Human Like Robot Ever) reveal one strategy of acceptance: narcissism or self-admiration.
The more robots look, act and behave like us, the more we forget that robots are separate and are not extensions of ourselves. While we ‘lose ourselves’ in the robot, we also lose sight of the potential dangers inherent in re-creating technological version of ourselves. Current scientific research is moving towards a functional humanoid capable of many human skills and communicative interaction. Herein lies the crux of the matter: when the optimal robot has been created it will become the model for reproduction. Once on the production line in the factory the robot will be mass produced.
So then will the concept of a ‘world where the robots did all the work, […] tend the crops, sew the clothes, cook the food, drive the trucks, and work on all the assembly lines in all the world’s factories’ come alive? Will people benefit? More and more people will be put out of work, even in jobs never considered threatened by technology before.
Will we have more leisure time? That is predicated on the idea of a social fund created by society to pay for education, health, transport etc. But where will that money come from? The beneficiaries of robot production (which will no doubt be private) will be the owners and shareholders of robot producing companies and factories supplying robots to universities, hospitals, libraries etc. not society as a whole.
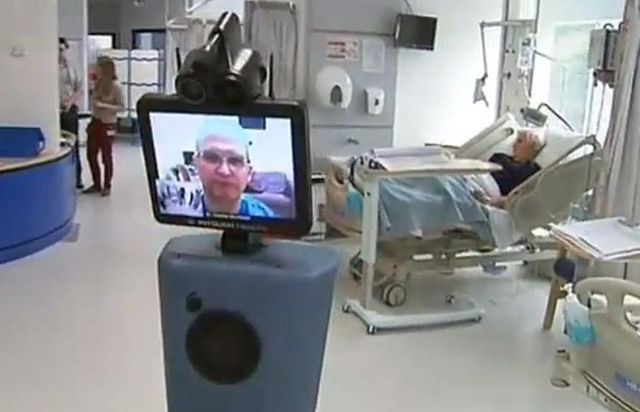
This may seem fantastical now during this transition phase of development but already relatively undeveloped robots are being used as tour guides and remote doctors. As more privatisation puts more people at the mercy of the profit motive, exposure to replacement by robot is only limited by the current capabilities of contemporary science.
Will things be cheaper? Many cars are made by robots but are not startlingly cheap because of competition (as competitors also have to invest in the same latest technology). Will there be an ‘abundance of stuff’? The planet already provides an abundance of stuff yet the World Bankestimated 1.29 billion people were living in absolute poverty in 2008. Can the planet keep providing an ‘abundance of stuff’? The process of resource depletion of finite raw materials would only be accelerated by an increased amount of robots working in more fully-automated factories.
One could argue that trades unions and professional associations would never let this happen yet redundancy and non-replacement of retired workers is opening up a gap which can be filled by sophisticated robots. Only stronger ties building on the common interest between the unemployed and employed can possibly resist this coming workplace crisis.
Notes
[1] Steven E. Jones, Against Technology: From the Luddites to Neo-Luddism (New York: Routledge, 2006) p.96
[2] See Luddite bicentenary resource site:
 http://www.ludditelink.org.uk/ and Chumbawamba’s English Rebel Songs 1381–1984 ‘The Triumph of General Ludd’
http://www.ludditelink.org.uk/ and Chumbawamba’s English Rebel Songs 1381–1984 ‘The Triumph of General Ludd’  https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cuBgeGKPGZI
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cuBgeGKPGZI [3] Friedrich Engels, Condition of the Working Class in England (1845). See:
 http://www.marxists.org/archive/marx/works/1845/condition-working-class/ch08.htm
http://www.marxists.org/archive/marx/works/1845/condition-working-class/ch08.htm [4] ‘Virtual receptionists replacing the real thing’ by John Dodge. See:
 http://www.smartplanet.com/blog/thinking-tech/virtual-receptionists-replacing-the-real-thing/3095
http://www.smartplanet.com/blog/thinking-tech/virtual-receptionists-replacing-the-real-thing/3095 [5]
 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_data_processing
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_data_processing [6]
 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LEO_%28computer%29
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LEO_%28computer%29 [7]
 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IBM
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IBM [8]
 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Desk_Set
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Desk_Set [9]
 http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0050307/
http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0050307/ [10]
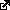 http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0063985/?ref_=fn_al_tt
http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0063985/?ref_=fn_al_tt [11]
 http://andrewmcafee.org/2013/04/mcafee-robots-work-employment-future/
http://andrewmcafee.org/2013/04/mcafee-robots-work-employment-future/ Caoimhghin Ó Croidheáin is a prominent Irish artist who has exhibited widely around Ireland. His work consists of paintings based on cityscapes of Dublin, Irish history and geopolitical themes (
 http://gaelart.net/). His blog of critical writing based on cinema, art and politics along with research on a database of Realist and Social Realist art from around the world can be viewed country by country at
http://gaelart.net/). His blog of critical writing based on cinema, art and politics along with research on a database of Realist and Social Realist art from around the world can be viewed country by country at  http://gaelart.blogspot.ie/.
http://gaelart.blogspot.ie/.
Caoimhghin Ó Croidheáin
 e-mail:
caoimhghin@yahoo.com
e-mail:
caoimhghin@yahoo.com
 Homepage:
http://gaelart.net/
Homepage:
http://gaelart.net/
Comments
Hide the following 2 comments
get a job programming computers
03.05.2013 22:16
plenty of jobs cant be replaced by robots. if you worried about it, get a job that isn't possible to be replaced by a computer or robot
joseph
Transformative
14.05.2013 19:35
The 1990 computerisation of the city of london, The-Big-Bang, is still not properly understood. Supercomputers that have Robot traders that auto trade stocks and shares. Short selling scum like Soros has made billions intentionally collapsing prices, then lame pension investing robots then auto sell leading to further collapse.
The computerisation of state services is the evilist of all. When they say efficiency savings they mean brutally refusing services, often picking on the weak.
In the future machines are going to transform construction, creating affordable housing. That will transform the cronic housing shortage, that make london unaffordable, and majorly disrupt the trillion dollar debt industry.
On the resource depletion of raw materials, since ww2 resources have trippled, and with new developments in Africa, Asia, and south America they WILL tripple again.
Rich